S.M.A.R.T. on Network Attached Storage (NAS)
1. General information
In general, NAS (Network Attached Storage) devices do not provide a readout function for S.M.A.R.T. data. From a user's point of view, it is possible to read and write files - but it is not possible to communicate the temperature and S.M.A.R.T. status of the hard disks externally via an interface or to generate an external warning in the event of critical problems. However, some NAS devices perform internal S.M.A.R.T. checks under the control of the NAS operating system.
With Argus Monitor and the S.M.A.R.T. on NAS feature discussed here, it is possible to monitor the hard disks of a NAS device in the same way as the internal PC hard disks are monitored and - in case of critical S.M.A.R.T. errors. - to generate warnings within Argus Monitor.
Argus Monitor can read the S.M.A.R.T. data of a NAS device under this condition:
- An instance of the Linux tool Smartmontools can be started cyclically on the NAS and this tools logs the S.M.A.R.T. data of the internal hard disks into a directory of the NAS.
- This directory is accessible from the Windows PC running Argus Monitor (network share), so Argus Monitor can read the data generated by Smartmontools.
Please note that our support for problems with S.M.A.R.T. access on NAS devices can only cover the topic
3. Configuration of Argus Monitor
For the topic
2. Configuration of NAS / Smartmontools (Synology Example)
please consult the help of your NAS device or corresponding forums on the internet.
Due to the diversity of NAS devices and NAS operating systems, we cannot provide support on this topic.
2. Configuration of NAS / Smartmontools (Synology Example)
- If necessary, install Smartmontools on your NAS. Consult the help for your device or corresponding forums on the Internet. On NAS devices of common manufacturers the Smartmontools are often already preinstalled, e.g. on Synology NAS devices.
- Open a command line on your NAS via SSH and determine the correct Smartmontools command to display the S.M.A.R.T. data. Please consult the Smartmontools help or appropriate forums on the internet in case of doubt. Note that Smartmontools requires sudo privileges to read the S.M.A.R.T. data.
Example for the first hard disk:
sudo smartctl -a -d sat /dev/sda
Example for the second hard disk:
sudo smartctl -a -d sat /dev/sdb
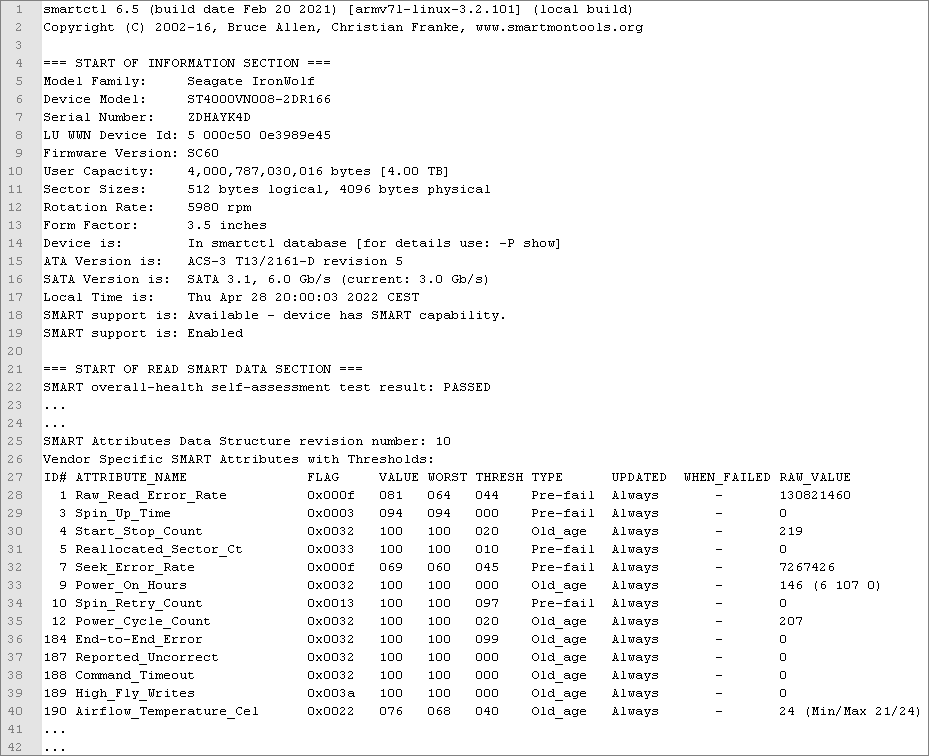
Example of a log file after successfully reading S.M.A.R.T. data using smartmontools:
- Create a directory on the NAS where the S.M.A.R.T. log files will be stored in the future, e.g. /Smart
- Schedule a task via the task scheduler of your NAS operating system that periodically writes the S.M.A.R.T. log files.
- Please make sure the generated log files start with smart_ (Argus Monitor will process only S.M.A.R.T. data files which start with this name).
- If there is no graphical task scheduler, such a task can alternatively be done via a cronjob (Linux knowledge required).
Example for task scheduling under Synology DSM 7 OS:
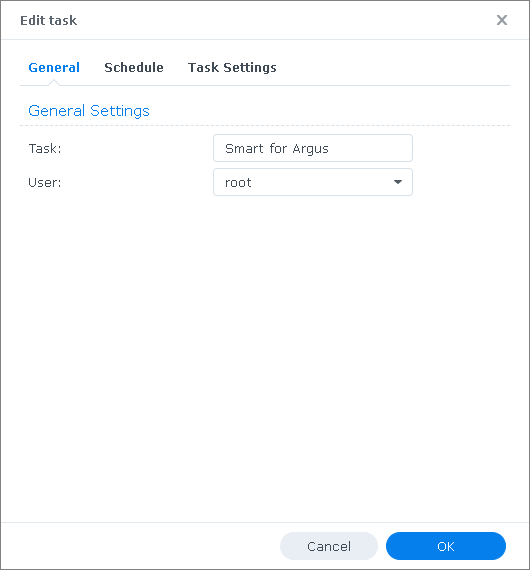
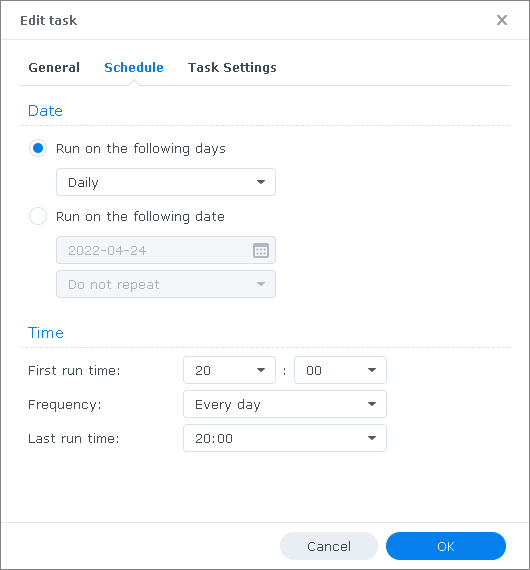
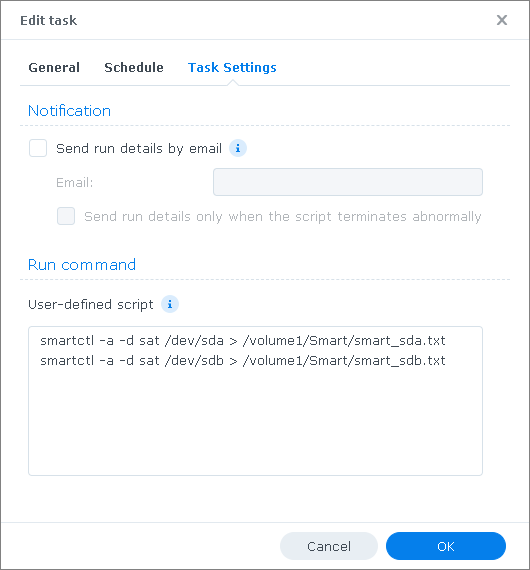
- After the task was executed, check if the log files with the S.M.A.R.T. data were generated in the directory \Smart:
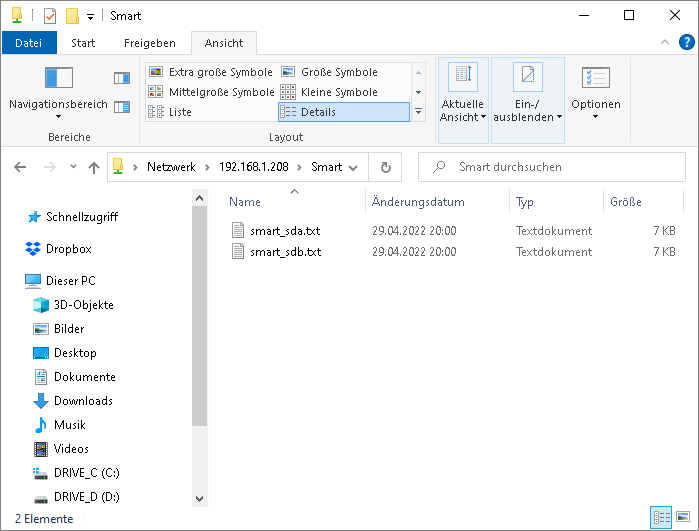
- In each S.M.A.R.T. file the different S.M.A.R.T. attributes must be present (in the section "Vendor Specific SMART Attributes with Thresholds", see picture at the beginning).
This completes the configuration on your NAS device.
3. Configuration of Argus Monitor
- In Argus Monitor Settings/S.M.A.R.T., enable S.M.A.R.T. over Network Attached Storage (NAS) and specify the location of the network share path where the S.M.A.R.T. data files are stored:
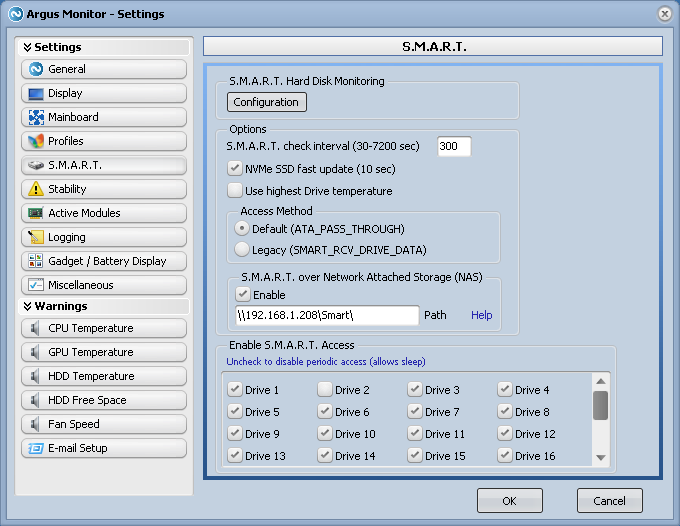
- Argus Monitor will scan this path within its default S.M.A.R.T. check interval and process the S.M.A.R.T. data from the NAS hard disk drives. If everything is successful, you will see these NAS drives in the same way you see the internal drives:
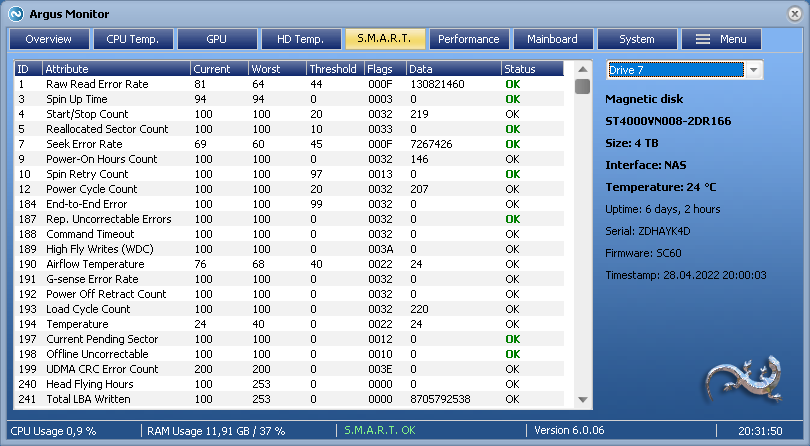
- In the screenshot, please note the Interface type NAS for these kind of drives.
- Please also note that the NAS log files are scanned by Argus Monitor in a fixed time interval of 10 min, not in the set user-defined interval for internal SSDs or hard disks. This has internal technical reasons and should be sufficient for detecting S.M.A.R.T. errors on a NAS in any case.
- Additional feature:
Argus Monitor also supports NAS devices which are not permanently powered on but are turned on/off only at certain times by user defined energy settings within the NAS operating system (e.g. for backup purposes).
To make this work, Argus Monitor will mirror by default all S.M.A.R.T. data files from the network share to the local directory c:\Users\<your user name>\AppData\Roaming\ArgusMonitor\.
In this local directory, all S.M.A.R.T. data files with an age of less than 3 days are considered valid. This way, drives from part-time powered off NAS devices will always show in Argus Monitor as long as they can be reached at least every 3 days.
The field Timestamp will show the time of the S.M.A.R.T. data.

